Top 5 Source Codes of the Common Exercises in C++
How to Learn C++ and What Makes It Different with C Programming Language?
I am going to show you how to nail those C++ programming common problems that you are encountering in every programming language exercises. I found these files in my old storage, so I will be sharing these C++ programming solutions to those who are eager to learn more about C++ or C programming. Sometimes, some of these exercises are used in laboratory exams or quizzes. Hence, it is way better to learn the strategies of these top 5 programming problems in C++ first and I guarantee you that the other high end programming languages will be easy for you to understand.
On the other hand, what makes C++ different with C programming language? And, can you use these C++ codes in C programming? C++ and C programming are almost the same, however, these 2 programming languages have evolved over time. C++ is actually the superset of C programming. C++ is a multi-paradigm programming language which is procedural and object oriented, unlike C programming which is only procedural. Thus, C++ can run almost all of C programming syntax while C has problems with C++ codes and you might be having difficulties in converting it. Moreover, you can use these codes that I will show you in C programming, but you should bear in mind that you have to change some of the correct syntax in the program. Furthermore, if you are a loyal C programmer then I suggest that you should make yourself comfortable with C++ as well because it has a lot of advancements than C.
My Source Code for the Top 5 Common Problems in C++ Programming
I am an avid fan of C++. First is, I like how it looks and how your creative mind runs when you create a simple animation out of the plain colorful pixelated shapes. Unlike some of the high-end programming languages with awesome GUI, you have to create your own looping codes and timer codes in C++ in order for you to create your own animation which is a lot of fun for me. It challenges my imagination. Second is, this is the first programming language that I have encountered and learned. Third is, I like the C++ syntax, maybe because this is the first programming language I have encountered and I am very comfortable with it. I like how to start and end the functions with braces. Thus, I like the simplicity of the looping technicalities and structure of C++ than the other programming languages. Furthermore, when I encountered Java, it became one of my favorite programming languages as well because it has similarities with the C++ structure. Programming in C++ is fun and you should try to learn c++ programming.
Table of Contents : Solutions for the C++ programming basics
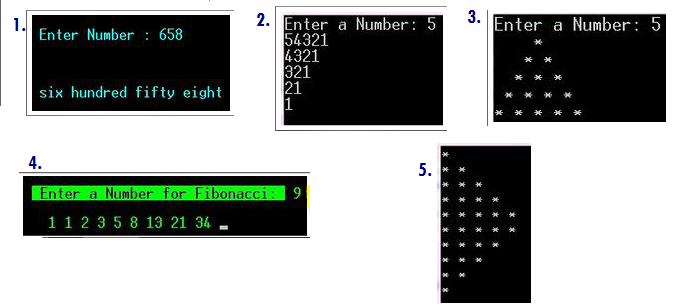
Problem #1 : Numbers to Text Conversion
Problem #2 : Descending Numbers Rotated Half Triangle Shape
Problem #3 : Descending Asterisk Chrismas Tree Shape
Problem #5 : Rotated Asterisk Christmas Tree Shape
You could use the links above to redirect you to the solutions below.
Problem #1 : Numbers to Text Conversion
Read an in-depth analysis of Problem # 1 on how to convert numbers to words. Kindly click the button below.
Breakdown of Codes ►
C++ : Numbers to Text Conversion
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
using namespace std;
void gotoxy(int x, int y)
{
HANDLE hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
COORD pos;
pos.X = x;
pos.Y = y;
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hConsole,pos);
}
int main(){
int a,b,c,d,e;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), 11);
gotoxy(20,12); cout << "Enter Number : ";
cin >>a;
gotoxy(20,16);
if (a==0){
switch (a)
case 0:
cout << " zero";}
e=a/1000;
if (e>=1 && e<10){
switch (e){
case 1:
cout << "one thousand "; break;
case 2:
cout << "two thousand "; break;
case 3:
cout << "three thousand "; break;
case 4:
cout << "four thousand "; break;
case 5:
cout << "five thousand "; break;
case 6:
cout << "six thousand "; break;
case 7:
cout << "seven thousand "; break;
case 8:
cout << "eight thousand "; break;
case 9:
cout << "nine thousand "; break;}
e=e*1000;}
a=a-e;
d=a/100;
if (d>=1 && d<10){
switch (d){
case 1:
cout << "one hundred "; break;
case 2:
cout << "two hundred "; break;
case 3:
cout << "three hundred "; break;
case 4:
cout << "four hundred "; break;
case 5:
cout << "five hundred "; break;
case 6:
cout << "six hundred "; break;
case 7:
cout << "seven hundred "; break;
case 8:
cout << "eight hundred "; break;
case 9:
cout << "nine hundred "; break;}
d=d*100;}
a=a-d;
b=a/10;
if (b>=2 && b<10){
switch (b){
case 2:
cout << "twenty"; break;
case 3:
cout << "thirty"; break;
case 4:
cout << "fourty"; break;
case 5:
cout << "fifty"; break;
case 6:
cout << "sixty"; break;
case 7:
cout << "seventy"; break;
case 8:
cout << "eighty"; break;
case 9:
cout << "ninety"; break;}
b=b*10;}
c=a-b;
if (c>=1 && c<10){
switch (c){
case 1:
cout << " one"; break;
case 2:
cout << " two"; break;
case 3:
cout << " three"; break;
case 4:
cout << " four"; break;
case 5:
cout << " five"; break;
case 6:
cout << " six"; break;
case 7:
cout << " seven"; break;
case 8:
cout << " eight"; break;
case 9:
cout << " nine"; break;}
}
if (a>=10 && a<20){
switch (a){
case 10:
cout << "ten"; break;
case 11:
cout << "eleven"; break;
case 12:
cout << "twelve"; break;
case 13:
cout << "thirteen"; break;
case 14:
cout << "fourteen"; break;
case 15:
cout << "fifteen"; break;
case 16:
cout << "sixteen"; break;
case 17:
cout << "seventeen"; break;
case 18:
cout << "eighteen"; break;
case 19:
cout << "nineteen"; break;}
}
getch ();
}
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
Problem #2 : Descending Numbers (Rotated Half Triangle Shape)
Read an in-depth analysis of Problem # 2 on how to create a function with descending numbers in a rotated half triangle shape. Kindly click the button below.
Breakdown of Codes ►
C++ : Descending Numbers
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
#include <iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define ct cout
void dec(int x);
int main() {
clrscr();
int x;
ct<<"Enter a Number: ";
cin>>x;
dec(x);
getch();
return 0; }
void dec(int x) {
int a,b;
for(a=x;a>=1;a--) {
for(b=a;b>=1;b--) {
ct<<b; }
ct<<endl; } }
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
Problem #3 : Ascending Asterisk (Christmas Tree Shape)
Read an in-depth analysis of Problem # 3 on how to print a christmas tree shaped asterisk by manipulating the length. Kindly click the button below.
Breakdown of Codes ►
C++ : Ascending Asterisk
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a,b,c,n;
cout<<"Enter a Number: ";
cin>>n;
for(a=1;a<=n;a++){
for(b=a;b<n;b++){
cout<<" ";}
for(c=1;c<=a;c++){
cout<<"* ";}
cout<<endl;}
getch ();
}
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
Problem #4 : Fibonacci
Read an in-depth analysis of Problem # 4 on how to create a Fibonacci numbers pattern in C++. Kindly click the button below.
Breakdown of Codes ►
C++ : Fibonacci
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
#include<windows.h>
using namespace std;
void gotoxy(int x, int y) {
HANDLE hConsole = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
COORD pos;
pos.X = x;
pos.Y = y;
SetConsoleCursorPosition(hConsole,pos); }
int Fibonacci(int num);
main (){
int num=0;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), 160);
gotoxy(23,10);
cout<<" Enter a Number for Fibonacci: ";
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), 10);
cout<<" ";
cin>>num;
Fibonacci(num);
gotoxy(25,12);
for(int i=1; i<=num; i++) {
cout << Fibonacci(i) <<" "; }
getch(); }
int Fibonacci(int num){
if (num==1||num==2){
return 1;}
else{
return Fibonacci(num-1) + Fibonacci(num-2);} }
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
Problem #5 : Asterisk (Rotated Christmas Tree Shape)
C++ : Asterisk Rotated Christmas Tree Shape
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
void myFunction(int start,int last);
void print(int x);
main (){
myFunction(1,5);
getch(); }
void myFunction(int start,int last){
print(start);
cout<<endl;
if(start<last) {
myFunction(start+1,last);}
print(start);
cout<<endl; }
void print(int x){
if(x>0){
print(x-1);
cout<<"*"<<" "; } }
//---www.skellainnovations.com---//
You may also visit C++ Programming : OOP << CLICK HERE